Pumping Systems: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Three types of pump systems: '''positive displacement''', '''momentum transfer''', and '''entrapment'''. | |||
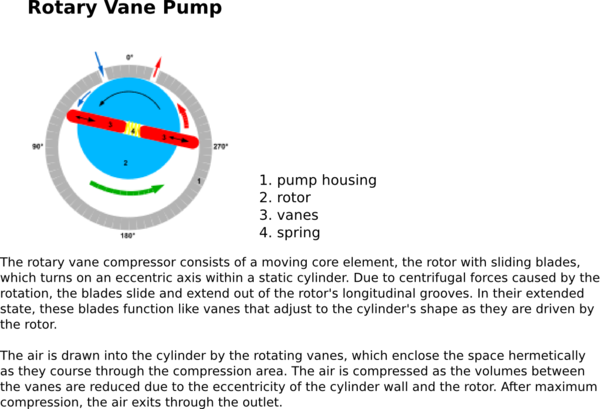
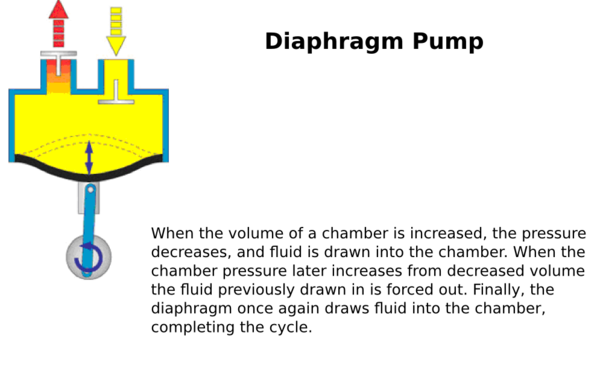
Positive displacement: Uses a mechanism to repeatedly expand a cavity, allow gases to flow in from the chamber, seal off the cavity, and exhaust it to the atmosphere. | == Positive Displacement Pumps == | ||
Positive displacement: Uses a mechanism to repeatedly expand a cavity, allow gases to flow in from the chamber, seal off the cavity, and exhaust it to the atmosphere. | |||
[[File:Rotary_vane_pump.png| 600px]] | |||
[[File:Diaphragm_pump.png|600px]] | |||
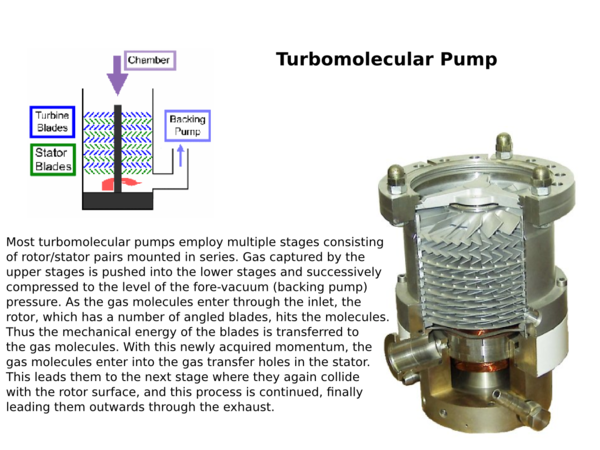
Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber. | == Momentum Transfer Pumps == | ||
Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber. | |||
[[File:Turbo_pump.png|600px]] | |||
== Entrapment Pumps == | |||
Capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state. | |||
[[File:Sorption_pump.png|600px]] | |||
'''Useful Links:''' | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotary_vane_pump| Rotary Vane Pump] | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diaphragm_pump| Diaphragm Pump] | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turbomolecular_pump| Turbomolecular Pump] | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sorption_pump| Sorption Pump] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:32, 7 November 2014
Three types of pump systems: positive displacement, momentum transfer, and entrapment.
Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement: Uses a mechanism to repeatedly expand a cavity, allow gases to flow in from the chamber, seal off the cavity, and exhaust it to the atmosphere.
Momentum Transfer Pumps
Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber.
Entrapment Pumps
Capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state.
Useful Links: